BECE 2022 Social Studies Past Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. Which of the following can aid economic independence of a nation?
Solution: Economic independence is achieved when a nation can sustain itself financially without relying heavily on external aid or imports. Generating enough revenue locally reduces dependency on foreign support.
2. Which of the following does not constitute a right of a Ghanaian according to the 1992 constitution?
Solution: The constitution guarantees rights such as personal liberty, life, and freedom of association, but unlawful assembly is not a protected right as it contradicts public order and safety.
3. The application of science to improve upon the quality of life or work is also known as
Solution: Technology refers to the practical application of scientific knowledge to solve problems or enhance human life and work.
4. The following activities bring disgrace to the people and Ghana as a whole except
Solution: The chieftaincy institution is a respected traditional system, while the other options involve harmful or illegal practices that tarnish Ghana’s image.
5. Which of the following activities is a duty of a citizen of Ghana?
Solution: Citizens have a duty to uphold and defend the constitution, which ensures national stability and governance.
6. Which of the following measures cannot improve the quality of life in the rural areas of Ghana?
Solution: Unregulated family planning can lead to overpopulation and strain resources, whereas the other options directly enhance living standards.
7. The early introduction of formal education by the colonialists in the Gold Coast, led to
Solution: Formal education provided skills that expanded the labour force, contributing to economic activities during the colonial era.
8. The following are aspects of culture except
Solution: While food is related to culture, it is a product of cultural practices, not an aspect itself. Beliefs, ceremonies, and language are core cultural elements.
9. The growth rate of Ghana’s population can be reduced mainly through
Solution: Family planning helps control birth rates, directly impacting population growth.
10. The revolution of the earth around the sun causes
Solution: The earth’s revolution around the sun results in seasonal changes due to the tilt of its axis.
11. The scale on the map is 200,000. If the distance on the map is 2 cm, find the actual distance on the ground?
Solution: Calculation: 2 cm × 200,000 = 400,000 cm = 4 km.
12. Why are laws made? For
Solution: Laws ensure conformity to societal norms and maintain order.
13. Which of the following is not an element of the weather?
Solution: Tides are oceanic phenomena influenced by the moon, not weather elements.
14. The safest place to save money is the
Solution: Banks are regulated institutions offering security for deposits.
15. Increasing opportunities for employment in the Ghanaian society can help to reduce
Solution: Employment reduces idleness and associated social vices like indiscipline.
16. Which of the following activities show interaction between the physical and social environments?
Solution: Breastfeeding is a social act influenced by the physical need for nourishment.
17. The Ghana Coat of Arms was designed by
Solution: Amon Kotei is credited with designing Ghana’s national emblem.
18. An account which is operated with the use of cheque, is known as
Solution: Current accounts allow cheque transactions for easy access to funds.
19. One of the ways of promoting unity among the ethnic groups in Ghana is through
Solution: Inter-ethnic marriages foster social cohesion and mutual understanding.
20. Which principle is used to check abuse of power in governance?
Solution: Separation of powers divides authority among branches to prevent concentration of power.
21. The savanna vegetation zones produce cattle because of the
Solution: Grasslands provide ample grazing land for cattle.
22. The process of identifying signals of conflict and encouraging people to work out their differences is known as conflict
Solution: Conflict management involves proactive measures to address disputes before escalation.
23. Which of the following factors can best make private sector businesses more profitable?
Solution: A ready market ensures consistent demand and revenue for businesses.
24. The colour blue is used on topographical maps to indicate
Solution: Blue conventionally represents water bodies on maps.
25. Which of the following does not reflect the importance of festivals in Ghana?
Solution: Festivals promote unity and development, not disputes.
26. One factor that can affect the academic performance of students negatively is
Solution: Truancy reduces study time and engagement in learning.
27. Laws in the country are made by the
Solution: Parliament is the legislative body responsible for enacting laws.
28. The statement scale 1cm to 5 km can be converted to representative fraction to read
Solution: 5 km = 500,000 cm, so 1 cm represents 500,000 cm (1:500,000).
29. The health of the people of Ghana can be improved through the
Solution: Sanitation directly reduces disease spread and improves public health.
30. For Ghanaians to come out of negative influence of colonial mentality, they should
Solution: Self-reliance fosters national pride and reduces dependency on colonial legacies.
31. Which of the following levies is imposed by the District Assemblies in Ghana?
Solution: Market tolls are local levies collected by District Assemblies for revenue.
32. The person who combines the factors of production such as land, labour and capital is called
Solution: Entrepreneurs organize resources (land, labour, capital) to create goods/services.
33. In Ghana, festivals usually serve all the following purposes except
Solution: Outdooring is a naming ceremony, not typically a festival activity.
34. Which of the following is associated with a scale of a map?
Solution: Linear scales graphically represent map-to-ground distance ratios.
35. The sole proprietor enjoys all the following advantages except
Solution: Unlimited liability is a disadvantage, as personal assets are at risk.
36. Which of the following factors is one of the major reasons for Ghana’s cultural diversity?
Solution: Migration introduced varied ethnic groups and traditions to Ghana.
37. Which of the following accounts for the presence of the equatorial forest in south-western Ghana?
Solution: High rainfall supports dense equatorial forests.
38. Food production in Ghana faces the problem of
Solution: Post-harvest losses reduce food availability due to poor storage/preservation.
39. Which of the following measures can increase tomato yield in Ghana?
Solution: Credit enables farmers to invest in quality inputs and technologies.
40. Ghana’s exports are highly dominated by
Solution: Ghana primarily exports raw materials like cocoa, gold, and oil.
1. (a) Draw an outline of the globe.
(b) On the outline of the globe, mark and label the following:
(i) Arctic Circle;
(ii) Tropic of Capricorn;
(iii) Latitude 0°;
(iv) Direction of Earth’s rotation;
(v) North Pole.
(c) (i) State two major highlands in Ghana.
(ii) State two major lowlands in Ghana.
(d) Outline two uses of International Dateline.
Solutions for Question 1
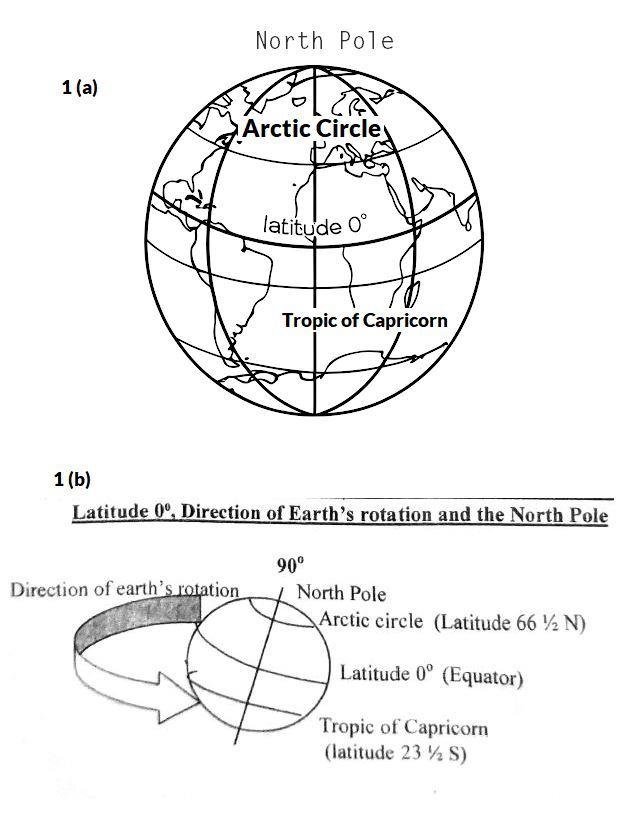
1.(c) (i) Major highlands in Ghana:
Gambaga Scarp (North East Highlands)
Mampong Scarp (Central Highlands)
Wa Scarp (North West Highlands)
Akwapim-Togo Ranges
Kwahu Scarp
(ii) Major lowlands in Ghana:
Volta Basin Lowlands
Coastal Lowlands/Plains
River Basins
1.(d) Uses of International Dateline:
Helps avoid confusion in time differences between places worldwide.
Determines days and nights at various locations at a specific time.
Determines dates in different parts of the world simultaneously.
Helps calculate local and standard time relative to GMT.
Informs travelers about gaining or losing a day when crossing time zones.
Divides the Earth into 24 time zones.
Its zigzag design prevents a single country from having two different dates.
2. The table below shows the population information of country X. Use the figures to answer the questions that follow:
| Age | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 0-17 | 10,815,000 | 54.4 |
| 18-59 | 8,836,000 | — |
| 60+ | 948,400 | 3.6 |
(a) Define the term population.
(i) The percentage of the working population of country X.
(ii) The total population of country X.
(c) Outline four disadvantages of Ghana's population structure.
Solutions for Question 2
2.(a) Definition of population: Population refers to the number of people living in a geographical area at a specific period or time.
2.(b) Calculations: (i) Percentage of working population (18-59 years):
Calculation: 100% - (54.4% + 3.6%) = 42%
Answer: 42%
(ii) Total population of country X:
Calculation: 10,815,000 + 8,836,000 + 948,400 = 20,599,400
Answer: 20,599,400
2.(c) Disadvantages of Ghana's population structure:
High government expenditure on social services (e.g., education, healthcare).
High dependency ratio (many dependents vs. working population).
Low savings and investment due to limited productive workforce.
Slow economic development from strained resources.
High pension costs for the aged.
Low tax revenue from a small working class.
Low productivity in key sectors.
High costs for training and retraining manpower.
3. (a) Explain the following terms associated with how Ghana cooperates with other countries:
(i) Political Cooperation;
(ii) Cultural Cooperation.
(b) In what four ways can Ghanaians help to maintain unity in their nation?
Solutions for Question 3
3.(a) Explanations: (i) Political Cooperation:
Ghana collaborates with other nations/international bodies (e.g., AU, UN, Commonwealth) to advance shared political interests.
(ii) Cultural Cooperation:
Ghana engages in cultural exchanges (e.g., PANAFEST, FIFA, Commonwealth Games) to showcase its heritage globally.
3.(b) Ways to maintain unity in Ghana:
Celebrating national festivals (e.g., Independence Day).
Encouraging inter-ethnic marriages.
Respecting diverse cultures and traditions.
Equitable distribution of national resources.
Political tolerance and dialogue.
Promoting indigenous music/dance in schools.
Discouraging ethnic stereotypes.
Public education on national cohesion.
4. (a) List four major ethnic groups in Ghana.
(b) Describe the migration routes of:
(i) Akans;
(ii) Ewes.
(c) Explain three factors that promoted ethnic migrations into Ghana.
Solutions for Question 4
4.(a) Major ethnic groups in Ghana:
Akan
Ewe
Ga-Adangbe
Mole-Dagbani
Guan
4.(b) Migration routes: (i) Akans:
Originated from the Old Ghana Empire.
Migrated via the Black Volta River to Offin-Pra Basin.
Settled in Techiman, Ashanti, Brong Ahafo, and coastal areas (e.g., Fante).
(ii) Ewes:
Traced ancestry to Oyo, Nigeria.
Migrated via Ketu (Benin) → Tado → Notsie (Togo).
Fled King Agorkoli to Ghana in 3 groups (Keta, Volta forests, mid-Volta).
4.(c) Factors for ethnic migrations:
Search for fertile land/farming opportunities.
Escape from conflict/wicked rulers (e.g., Agorkoli).
Economic pursuits (trade, fishing).
Natural disasters (drought, famine).
Population pressure.
5. (a) Define the following:
(i) Human settlement;
(ii) A slum.
(b) What four benefits do people derive from touring different places?
(c) State four uses of land in your community.
Solutions for Question 5
5.(a) Definitions: (i) Human settlement: A place where people establish homes to live.
(ii) Slum: Overcrowded, disorderly, and unsanitary area inhabited by the poor.
5.(b) Benefits of touring:
Sightseeing/nature appreciation.
Educational/research opportunities.
Health/relaxation benefits.
Religious pilgrimages.
Cultural exchange.
Souvenir collection.
5.(c) Uses of land:
Farming.
Housing.
Transportation (roads).
Mining.
Grazing.
Industrial sites.
Schools/hospitals.
Burial grounds.
6. (a) List two examples of primary economic industries in Ghana.
(b) Highlight three problems facing the primary economic industry in Ghana.
(c) What four measures can improve the primary economic industry in Ghana?
Solutions for Question 6
6.(a) Primary industries:
Farming.
Fishing.
Mining.
Lumbering.
6.(b) Problems:
Poor storage/post-harvest losses.
Inadequate credit for farmers.
Erratic rainfall/irrigation issues.
High cost of farm inputs.
Land tenure conflicts.
6.(c) Improvement measures:
Irrigation development.
Better road networks.
Accessible credit/subsidies.
Modern storage facilities.
Cooperative societies.
Stable government policies.